When Google rolled out AI Overview and, most recently, AI Mode, the familiar naysayers showed up. This time, SEO is really done for, they cried, and there was much wailing and gnashing of teeth (we’re a dramatic bunch, marketers). So, is it true? Is SEO kaput for real this time? Will content marketing be caught in the crossfire?
In a word, no.
But generative search overviews have dramatically shifted search behavior. Click-throughs and organic traffic are down across the board, with an average of 34.5% when AI Overviews are present, according to Ahrefs. However, while clicks are down, impressions are up. Backlinko reported a 15% decrease in clicks over 3 months, but a 54% increase in impressions. So, what gives? Brands are showing up in generative search, and even though a consumer might not click right away, AI makes a huge brand impression.
As a result, brands want to know how to improve visibility in the AI Overview or the host of other AI chatbots like ChatGPT or Perplexity. This demand has given rise to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), the art of getting seen by AI bots. GEO has changed the game, but the good news is that many of the “rules” that serve as guidelines for SEO are still relevant in generative search. Quality, media-rich content is still likely to appear in both traditional search and AI Overviews.
However, there are a few tricks to getting seen and cited by AI. This post goes over a few of them. But first, let’s take a closer look at history to help us understand the present situation.
Also read: The Best Time to Send B2B Emails: Timing Strategies That Drive Engagement
A quick history of SEO
- The 90s: Search engines were born. With the advent of PageRank, its search algorithm that ranks pages by quality and backlinks, Google became the dominant search engine in the latter part of the decade.
- The 2000s: Google introduced updates to counter black-hat SEO techniques, such as keyword stuffing. In 2007, they introduced Universal Search, which looped in images, videos, news, and local listings into search results.
- The 2010s: Google introduced numerous updates (that caused marketers to declare SEO was dead). The 2019 BERT update laid the foundation for natural language processing (NLP), a key aspect of generative AI.
- The 2020s: Generative AI has sparked a revolution in search that gave way to GEO.
GEO, the story so far
Google launched its AI Overview (originally called Search Generative Experience or SGE) in May of 2024. Almost immediately, brands wanted to figure out how to show up in AI Overview searches, and GEO was born as a result.
ChatGPT was not far behind in launching SearchGPT, its answer to AI Overview. This tool can search the web from inside the ChatGPT interface. The other major AI players soon followed suit.
At first, there were… hiccups. AI Overview sometimes gave nonsense answers after sourcing information from highly ranked satire websites like The Onion. While generative search has improved since claiming glue was an appropriate thickener for pasta sauce, it’s still evolving.
AI Mode, Google’s latest development, offers users an interface more like ChatGPT or other Large Language Models (LLMs). The most significant difference between traditional search and AI Mode is that it displays selective or no URLs in its answers.
GEO vs SEO: Key differentiators
| Aspect | SEO | GEO |
| Goal | Rank highly on the first page of Google and drive traffic to a brand’s website. | Generative search is about answering user questions with authority. GEO is about appearing in those answers. |
| Strategies | Best practices include keyword optimization, backlink building, mobile responsiveness, and fast website speeds. | Build on SEO strategies, focusing on how LLMs answer and interpret questions. |
| Desired outcome | Increase clickthroughs to blogs and websites, ultimately leading to purchases. | Improve visibility and engagement with the brand. Clicks are less critical than visibility in GEO. |
Benefits of GEO
So, if many of the same SEO principles work for GEO, why pay attention to them (versus going all-in on SEO)? GEO is simply the way things are going in marketing. But beyond that, there are real benefits to strategizing GEO.
A leveled playing field
In SEO, if your web page doesn’t show on the first page of Google, it may as well not even exist. There’s an old SEO joke: Where do you hide a dead body? The second page of Google results.
However, in GEO, rankings are far less critical. The priority is answering the user’s question, regardless of where it comes from. In fact, SEMrush found that most generative search results included citations from web pages on the 21st or higher page of Google Search results.
This makes it easier for smaller brands with fewer resources to get mentioned in AI Overviews and other generative search functions, provided they know how to optimize their content for AI (more on this below).
Build higher brand impressions without clicks
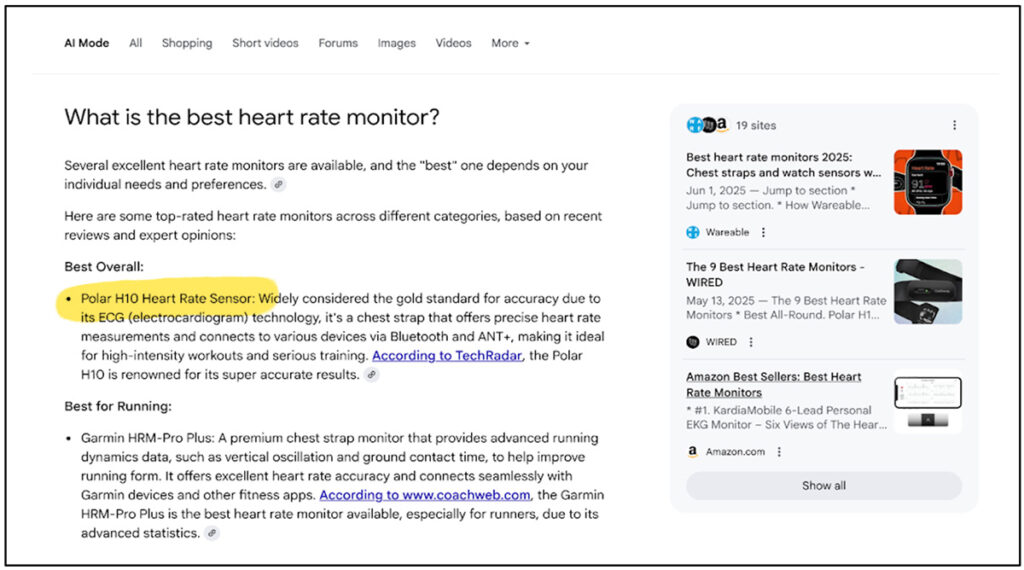
As mentioned previously, users aren’t necessarily clicking at the same time they search for the answer to a question in AI search. Let’s say you are looking to buy a heart rate monitor. You search: “What is the best heart rate monitor?” Interestingly, at the time of writing this blog, there isn’t an AI Overview for this search (research suggests that roughly 92% of keywords/keyword phrases still don’t have AI overviews). So, we turn to AI Mode.
AI Mode breaks down the buying journey into several considerations and mentions a few brands and links to several review websites:
In this example, if I’m looking for a budget-friendly monitor, I might jot down the Polar H10 monitor and return to it later.
How to show up in AI search results

While generative search is constantly evolving, there are several types of content we know generative AI loves:
- FAQs: Generative search is all about answering user questions. An FAQ section or FAQ post is an easy way for AI to pull an answer from your site. Additionally, answering common user questions in your niche helps establish you as a trusted source.
- Charts/Graphs: AI loves proof. Providing evidence with charts, tables, or graphs can significantly increase your chances of not only showing up in citations, but also getting linked to.
- Stats: Including statistics from trusted sources in your posts helps signal to AI that you are also a trusted source. Investing in original research can go a long way in establishing authority with AI and showing up in multiple queries. (Original research also has the added benefit of building backlinks in traditional SEO.)
- Rich media: Increasingly, AI search results include images and videos. This means that long-time SEO strategies like syndicating and repurposing content across platforms and creating video summaries of blog posts have found new life with GEO.
- Comparison posts: Notice that the above example of the heart rate monitor didn’t feature links directly to brand websites. AI prefers to add links to comparison posts by Wired and Tech Radar. If you can get featured in a post like this, great. But you may consider authoring similar posts, even if they don’t directly feature one of your products or services (an old principle of content marketing, value over selling).
Case study: See how Blue Star helped our client both rank highly in SEO and appear in AI Overviews for critical searches: Achieving top SEO and SERP rankings with a targeted keyword strategy – Blue Star
Blazing Trails in GEO

Beyond these specific content types that AI craves, some broader strategies and shifts in thinking apply directly to GEO.
- Semantic SEO: Keywords continue to lose importance. Does that mean we should forget about them? Not exactly. Instead, consider keyword research as topic research and keep lists of semantically related phrases. Include these phrases in your posts. For example, with our heart rate monitor post, we might include related keywords that rank well, such as “fitness tracker,” or questions such as “how can I track my steps?”
- Search everywhere optimization: The most significant shift in SEO vs GEO is decentralizing Google. Don’t get me wrong; Google is still THE search engine, but both users and AI are going to numerous platforms to make buying decisions. Consumers may start with AI Overviews to get the lay of the land, look at Amazon reviews, and then consult Reddit for more targeted questions or testimonials.
- Structured data: Strategically structuring data makes AI more likely to read and use it. This is known as Schema, and there are specific WordPress plugins that you can use to automatically structure your data in an AI-friendly way.
How to measure AI search results?
The short answer: you don’t.
The longer answer is, with a lot of reverse engineering. The only surefire way to know if your brand appears in AI Overviews or ChatGPT is to query them for related searches.
A few tools, like LLMrefs, can show you what brands are being mentioned in keyword searches by AI engines. However, they are new and still a little wonky. Also, you can track traffic from LLMs using GA4, but it takes a lot of tinkering and guesswork.
As GEO evolves, so will the methods of tracking visibility in generative engines.
Learn more about navigating GA4 in our recent blog post: GA4 basics: How to Escape the Chaos and Find Clarity
A zero-click future?
SEO isn’t dead. Not yet, anyway. What we’re seeing now in search isn’t a battle of SEO vs GEO. Rather, GEO is the natural evolution of SEO principles that emerged over the past three decades.
Will generative search lead to the end of content marketing and even the end of websites in general? Maybe. For now, AI needs websites, blog posts, and videos to craft its answers. And many searches still don’t have AI Overviews.
As clicks lose importance, visibility in AI will be key.
Need help planning your GEO strategy? We can help. Drop us a line.

